Owning a home is a cornerstone of financial security, yet not all homes are financed the same way. Manufactured homes—sometimes called mobile homes or prefab homes—have unique characteristics that affect how lenders provide financing. Understanding manufactured home mortgages, mobile home financing, and prefab loans can help prospective buyers make informed decisions.
What Is a Manufactured Home Mortgage?
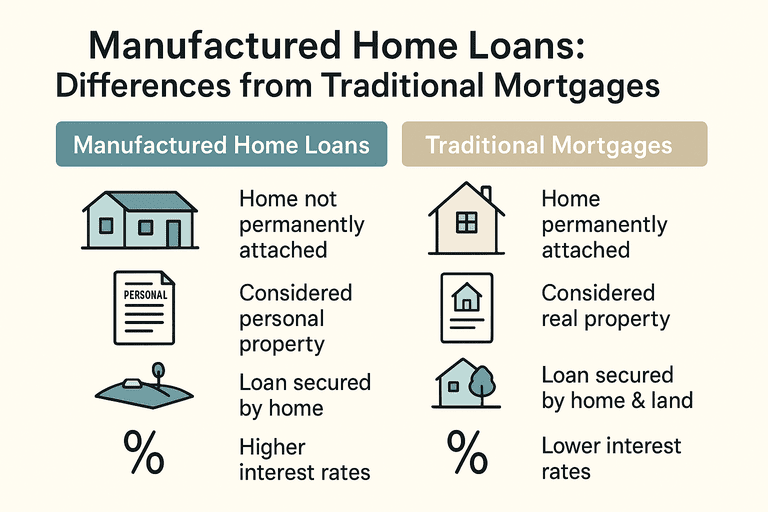
A manufactured home mortgage is specifically designed for homes built in a factory and transported to a permanent location. Unlike conventional mortgages, these loans account for the home’s mobility, structure, and classification.
Key differences from traditional home loans include:
Classification: Manufactured homes may be personal property if not permanently affixed to land, impacting loan types.
Loan Term: Terms are often shorter than traditional mortgages, sometimes 15–25 years instead of 30.
Interest Rates: Rates may be slightly higher due to perceived risk, particularly for homes not permanently attached to land.
Down Payment Requirements: Often range from 5% to 20%, depending on loan type and lender.
Mobile Home Financing Options
Prospective buyers have several avenues for financing a mobile or manufactured home:
1. FHA Title II Manufactured Home Loans
The Federal Housing Administration (FHA) provides insured loans for eligible manufactured homes. Features include:
Low down payment requirements (as low as 3.5%)
Long loan terms (up to 30 years for certain setups)
Eligibility for both home and lot financing
2. VA Loans for Veterans
For veterans, VA loans can finance manufactured homes if the home meets foundation and safety standards. Benefits include:
No down payment
Competitive interest rates
No private mortgage insurance (PMI)
3. Conventional Manufactured Home Mortgages
Traditional banks and credit unions may offer conventional loans if the home:
Is permanently affixed to land
Meets FHA or local building codes
Passes appraisal requirements
4. Prefab or Modular Home Loans
Prefab loans can be used for homes constructed offsite but assembled on a permanent foundation. These loans resemble traditional mortgages in terms of terms and interest rates but are tailored to offsite construction timelines.
Key Differences Between Manufactured and Traditional Mortgages
| Feature | Manufactured Home Mortgage | Traditional Mortgage |
|---|---|---|
| Home Type | Factory-built, sometimes mobile | Site-built |
| Loan Term | 15–25 years common | Up to 30 years |
| Down Payment | 5–20% | 3–20% |
| Interest Rates | Slightly higher on personal property | Standard rates |
| Collateral | Home only or home + land | Land + home |
Advantages of Manufactured Home Financing
Financing a manufactured home can offer several benefits:
Affordability – Lower purchase prices make homeownership more accessible.
Flexibility – Financing options exist for both mobile and land-based homes.
Faster Construction – Prefab homes are quicker to build than site-built houses, potentially reducing loan disbursement time.
Variety of Loan Programs – Government-backed loans (FHA, VA) increase access for buyers with lower credit scores.
Challenges to Consider
While there are advantages, buyers should also account for potential challenges:
Higher Insurance Costs – Mobile homes can carry higher premiums due to vulnerability to weather.
Land Ownership – If the home is not on owned land, lenders may treat it as personal property, limiting loan options.
Resale Value – Manufactured homes may depreciate faster than site-built homes, impacting equity growth.
Lender Availability – Not all lenders provide manufactured home financing, requiring additional research.
Tips for Securing the Best Manufactured Home Loan
Research Loan Types – Compare FHA, VA, conventional, and prefab-specific loans.
Check Home Classification – Ensure the home is eligible for your chosen loan type (personal property vs. real estate).
Understand Additional Costs – Include land purchase, site prep, and insurance.
Work with Experienced Lenders – Find lenders familiar with manufactured and modular home financing.
Plan for Appraisal and Inspection – Lenders typically require verification that the home meets safety and foundation standards.
Conclusion
A manufactured home mortgage provides an alternative path to homeownership for those seeking affordability, flexibility, and quick construction. By exploring mobile home financing and prefab loan options, buyers can choose a program that fits their financial goals while navigating the unique aspects of factory-built homes. Knowledge of loan differences, eligibility requirements, and potential challenges is crucial to secure the right financing.
For more detailed guidance, mortgage calculators, and loan comparisons, visit CalculatingAMortgageLoan.com.
Sources: